Topology
Kiali offers multiple ways for users to examine their mesh Topology. Each combines several information types to help users quickly evaluate the health of their service architecture.
Overview
Kiali’s default page is the topology Overview. It presents a high-level view of the namespaces accessible to Kiali, for this user. It combines service and application information, along with telemetry, validations and health, to provide a holistic summary of system behvior. The Overview page provides numerous filtering, sorting and presentation options. From here users can perform namespace-level Actions, or quickly navigate to more detailed views.
Graph
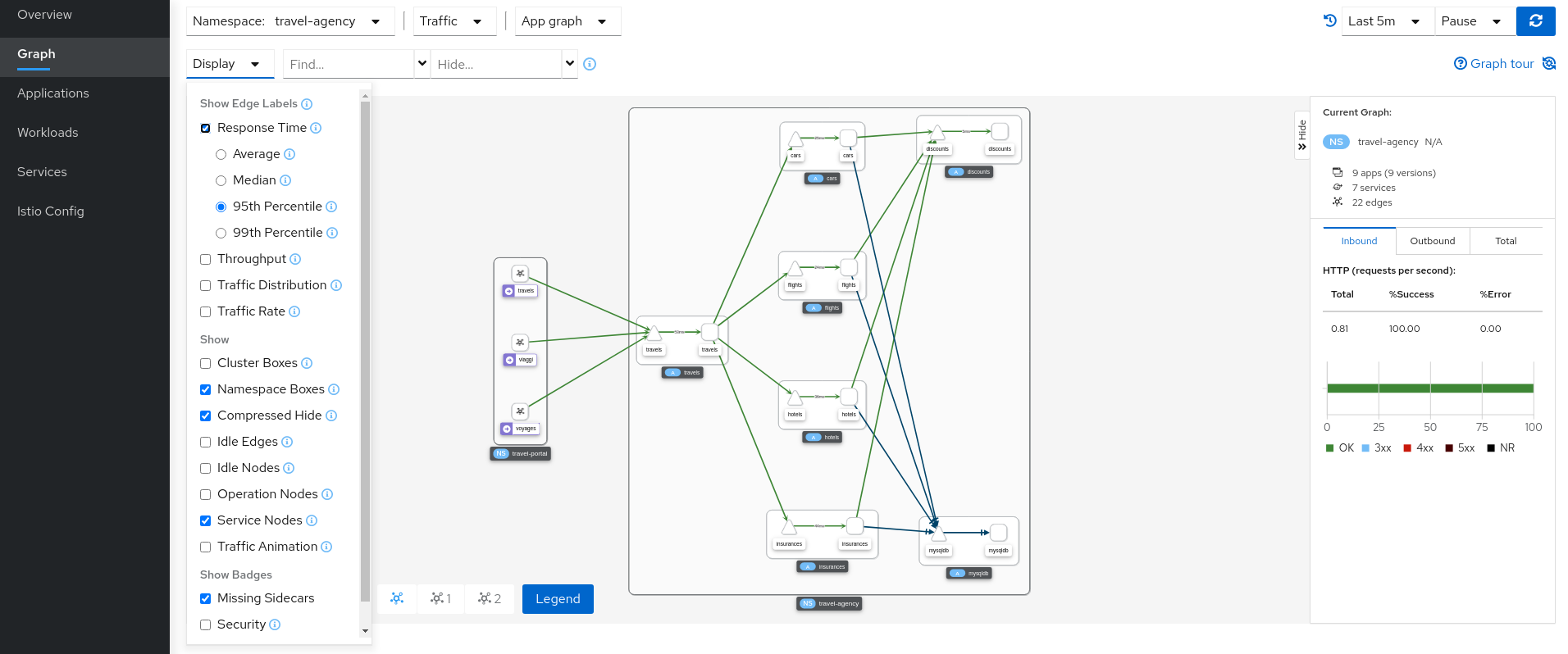
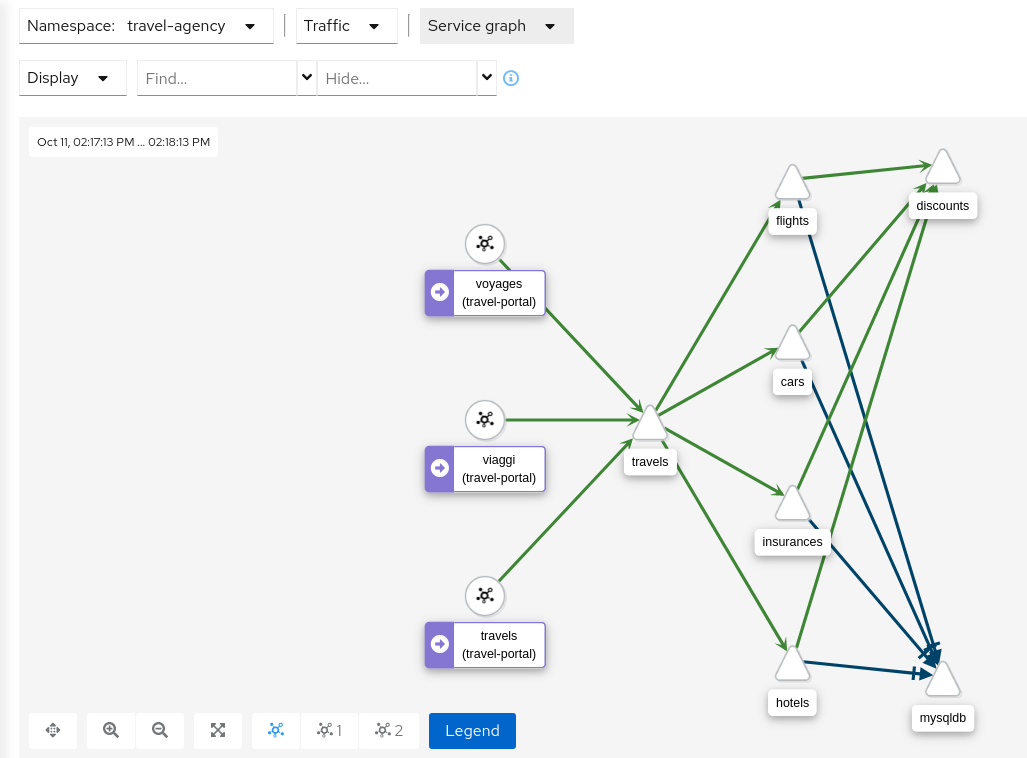
The Kiali Graph offers a powerful visualization of your mesh traffic. The topology combines real-time request traffic with your Istio configuration information to present immediate insight into the behavior of service mesh, allowing you to quickly pinpoint issues. Multiple Graph Types allow you to visualize traffic as a high-level service topology, a low-level workload topology, or as an application-level topology.
Graph nodes are decorated with a variety of information, pointing out various route routing options like virtual services and service entries, as well as special configuration like fault-injection and circuit breakers. It can identify mTLS issues, latency issues, error traffic and more. The Graph is highly configurable, can show traffic animation, and has powerful Find and Hide abilities.
You can configure the graph to show the namespaces and data that are important to you, and display it in the way that best meets your needs.
Health
Colors in the graph represent the health of your service mesh. A node colored red or orange might need attention. The color of an edge between components represents the health of the requests between those components. The node shape indicates the type of component such as services, workloads, or apps.
The health of nodes and edges is refreshed automatically based on the user’s preference. The graph can also be paused to examine a particular state, or replayed to re-examine a particular time period.
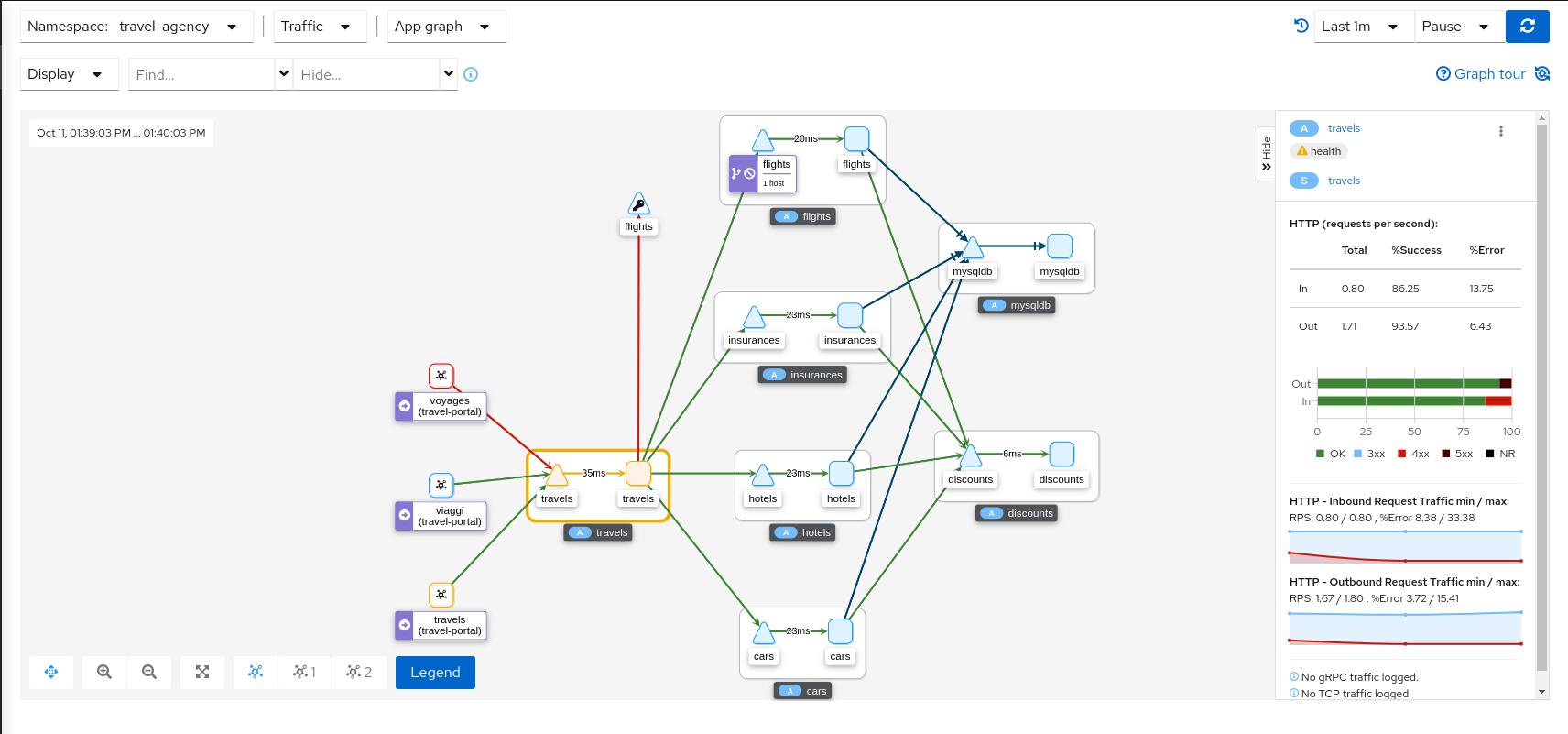
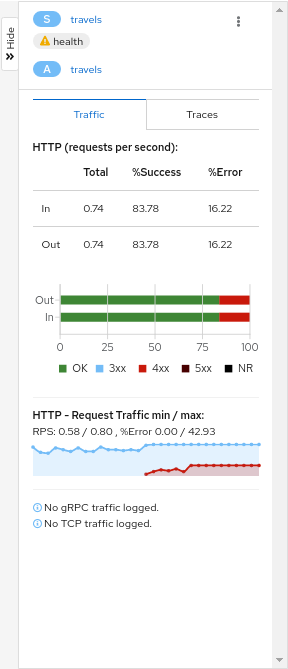
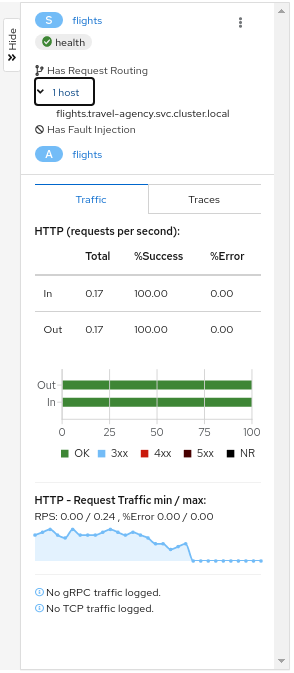
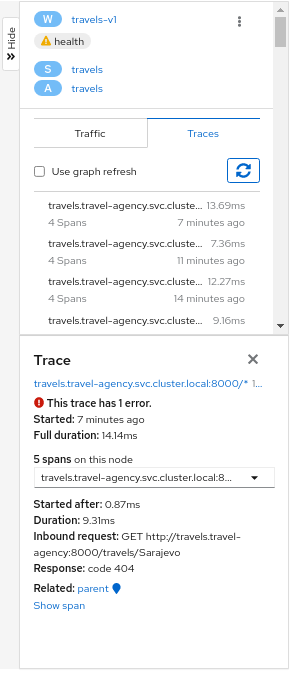
Side-Panel
The collapsible side-panel summarizes the current graph selection, or the graph as a whole. A single-click will select the node, edge, or box of interest. The side panel provides:
- Charts showing traffic and response times.
- Health details.
- Links to fully-detailed pages.
- Response Code and Host breakdowns.
- Traces involving the selected component.
Node Detail
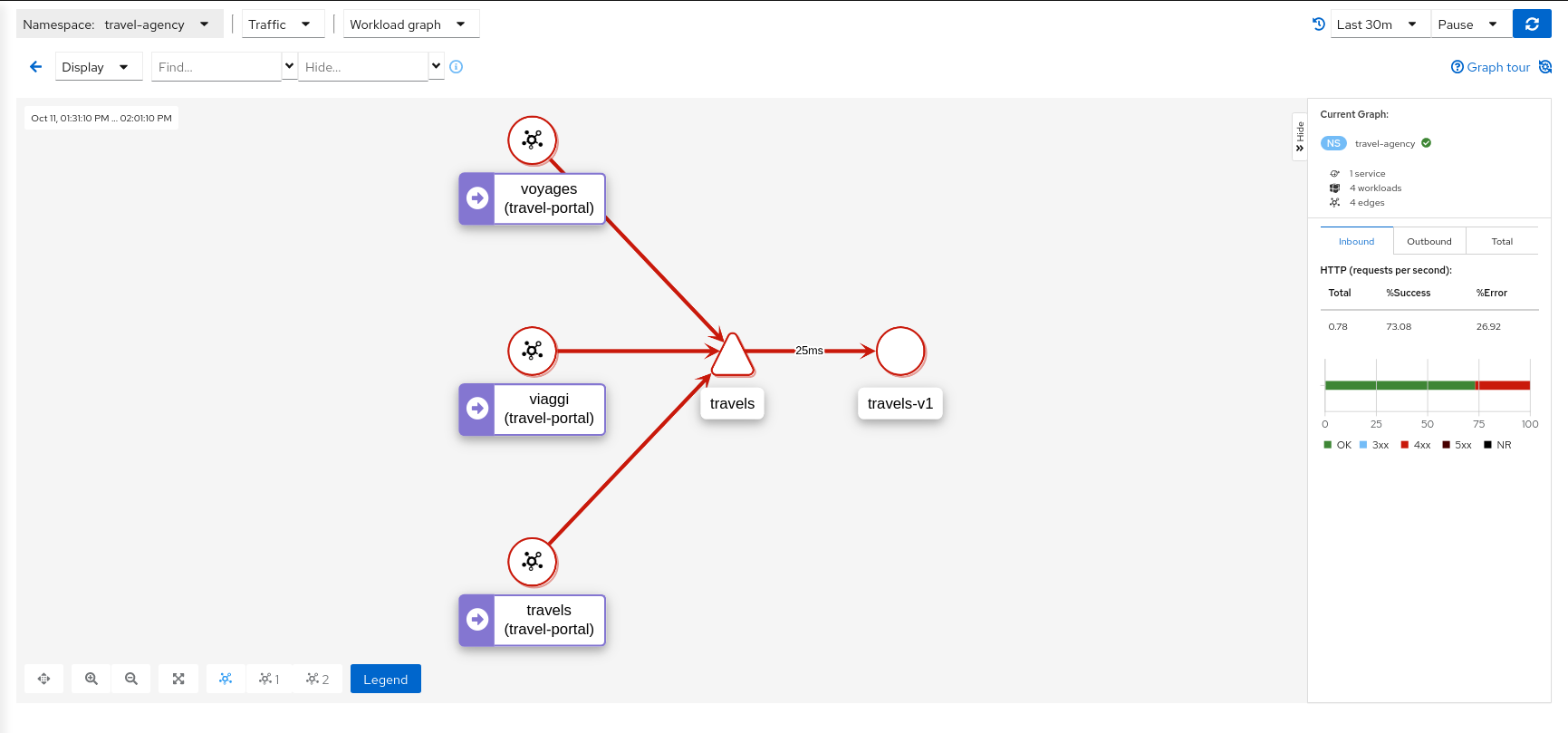
A single-click selects a graph node. A double-click drills in to show the node’s Detail Graph. The node detail graph visualizes traffic from the point-of-view of that node, meaning it shows only the traffic reported by that node’s Istio proxy.
You can return back to the main graph, or double-click to change to a different node’s detail graph.
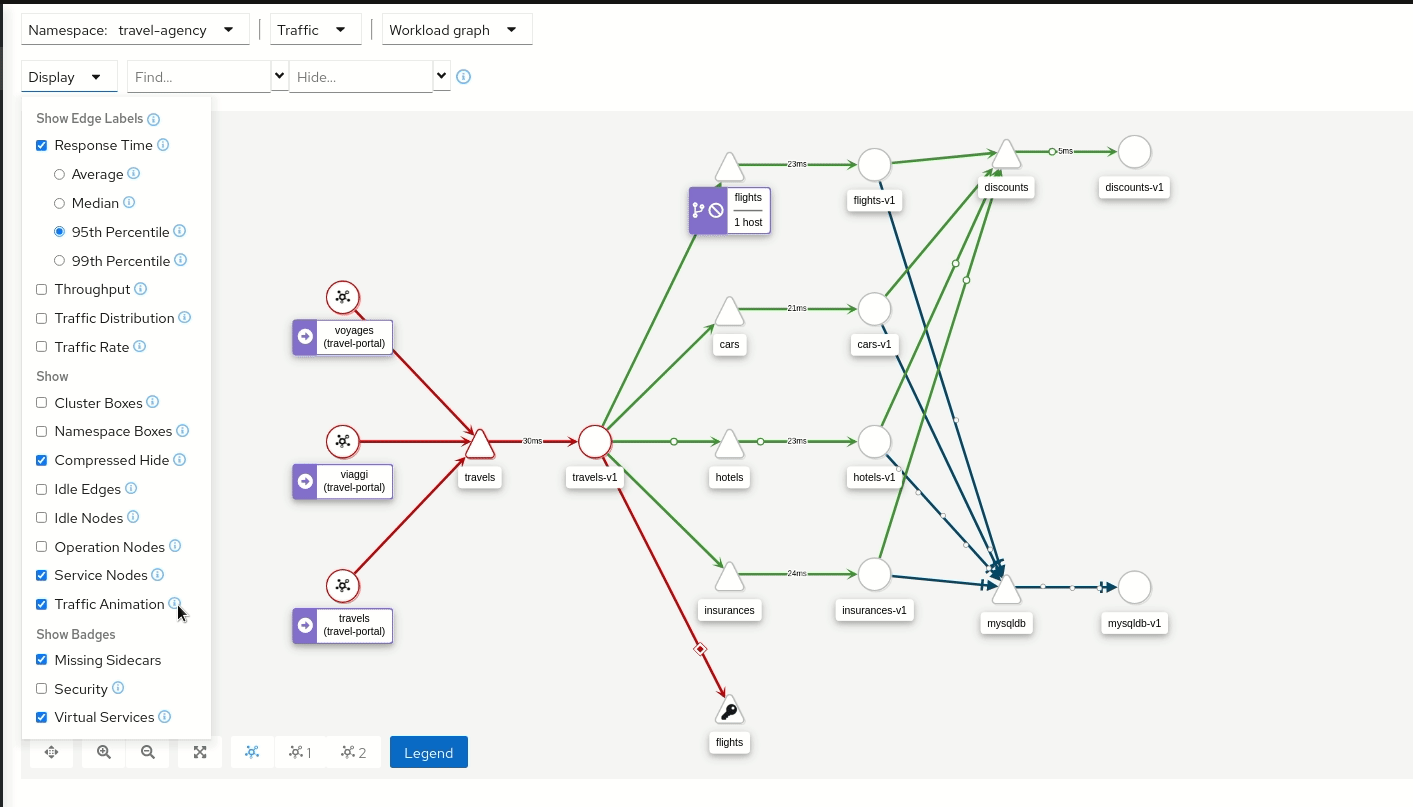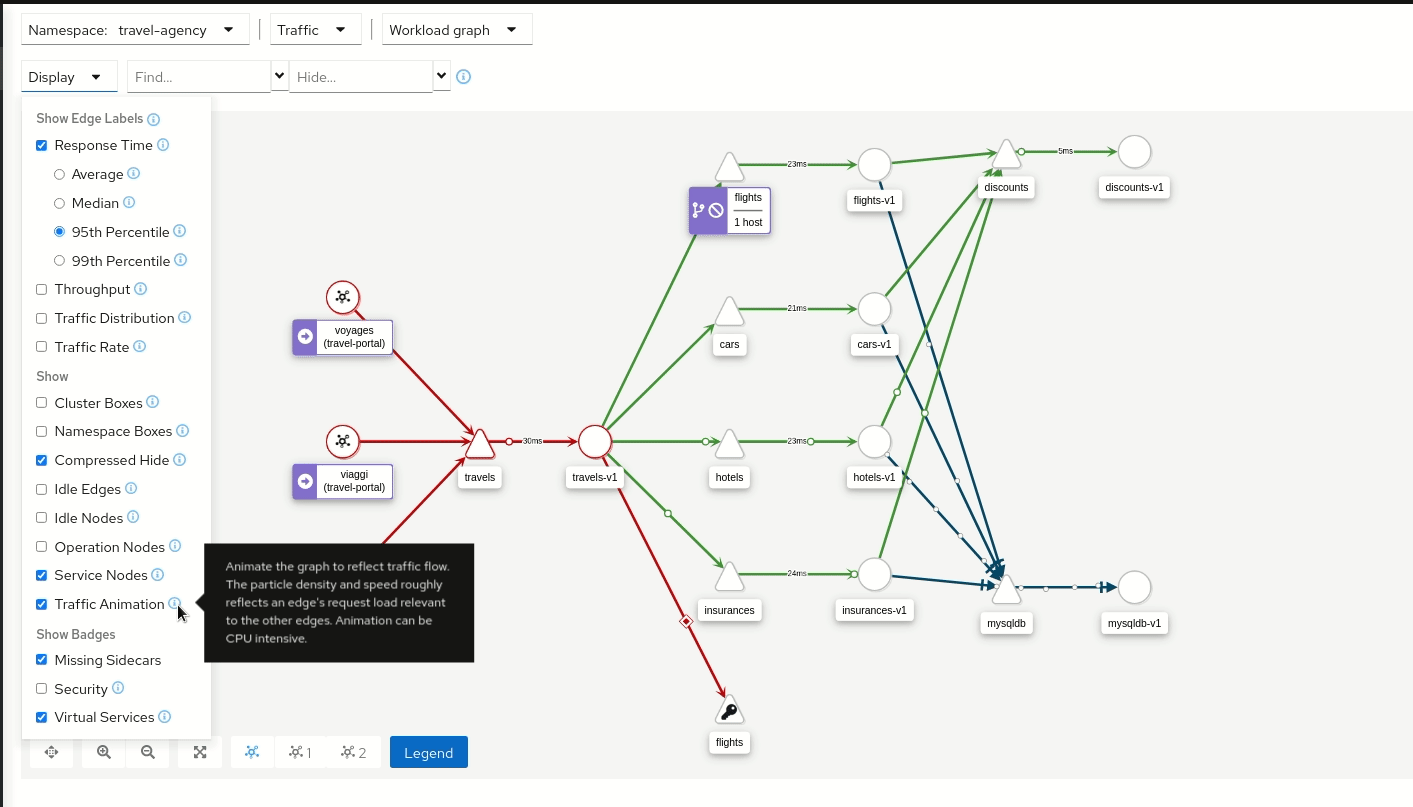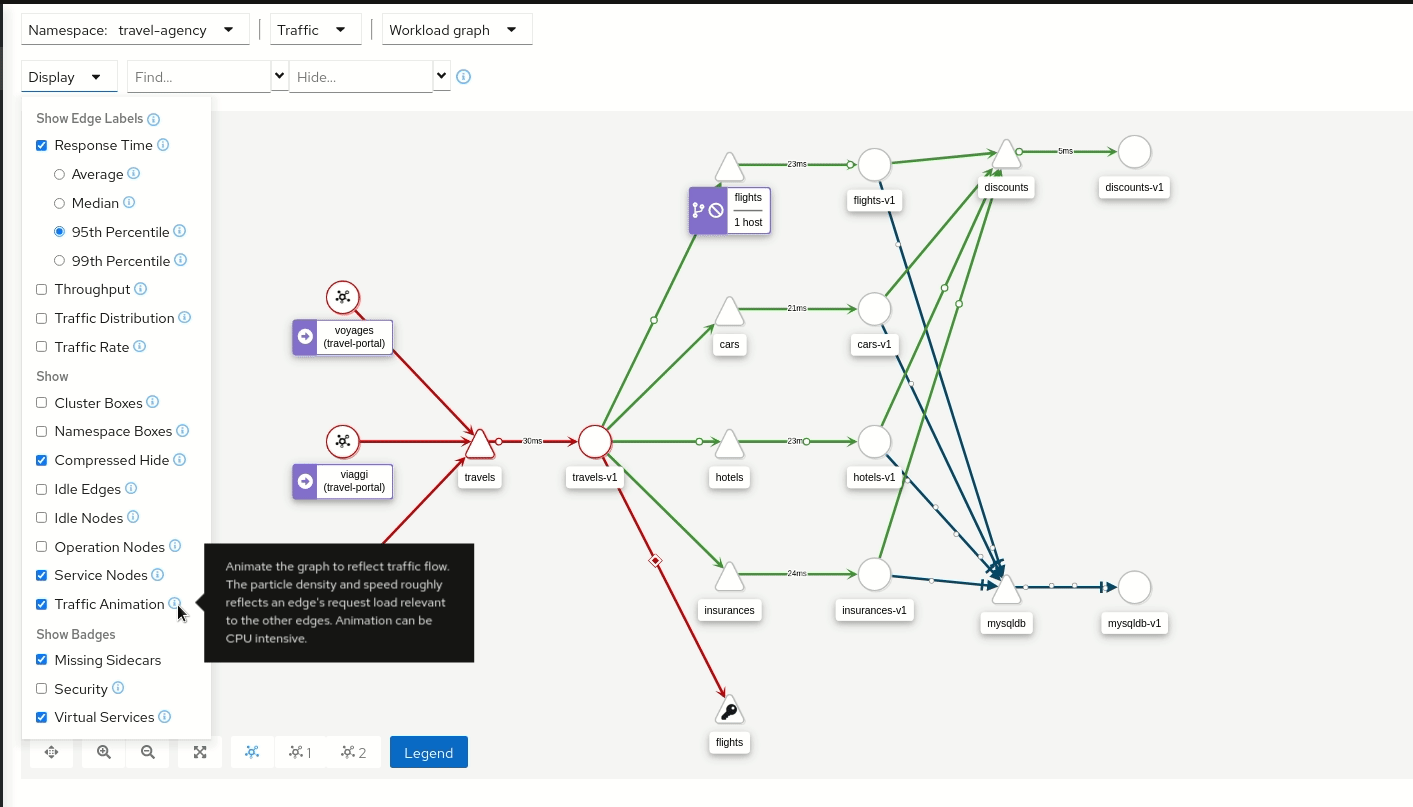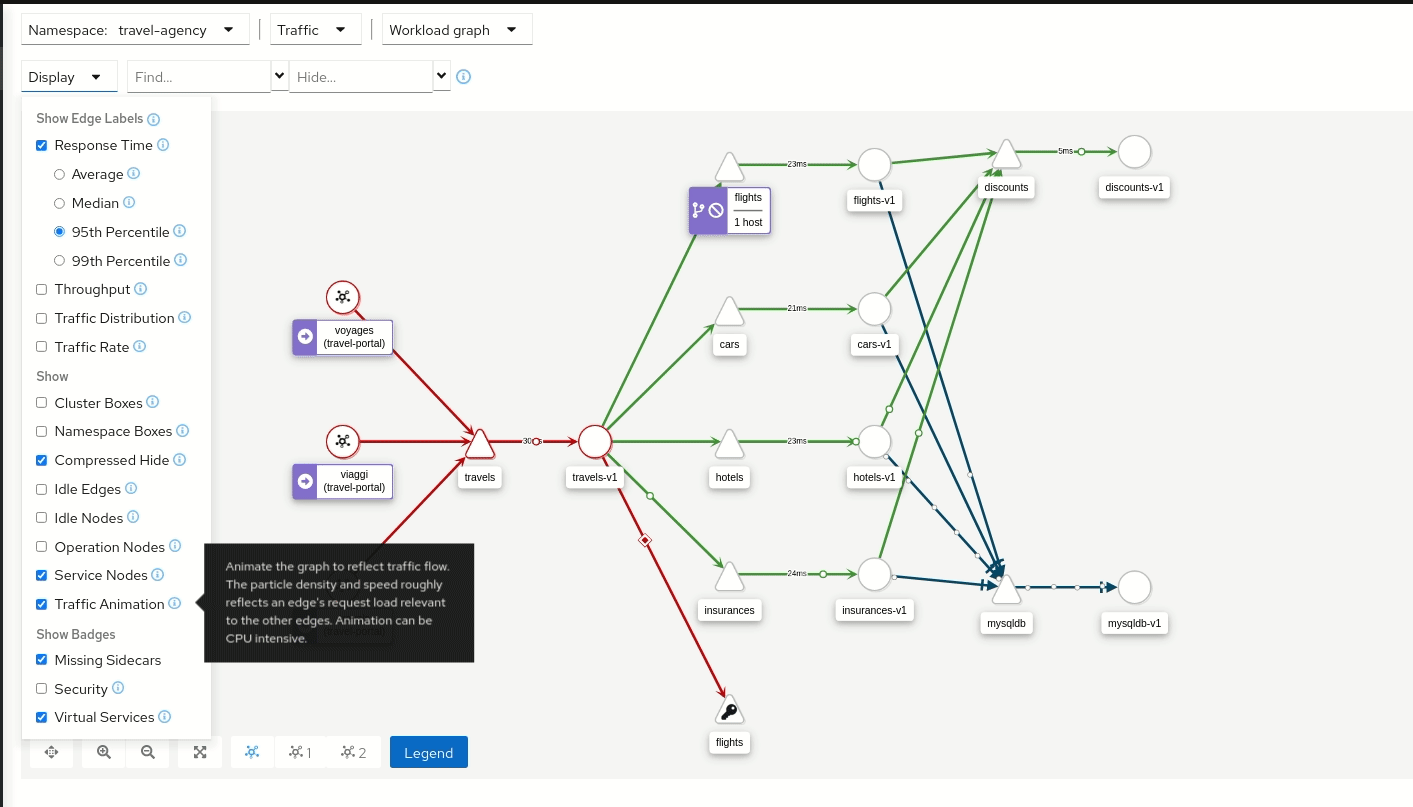
Traffic Animation
Kiali offers several display options for the graph, including traffic animation.
For HTTP traffic, circles represent successful requests while red diamonds represent errors. The more dense the circles and diamonds the higher the request rate. The faster the animation the faster the response times.
TCP traffic is represented by offset circles where the speed of the circles indicates the traffic speed.
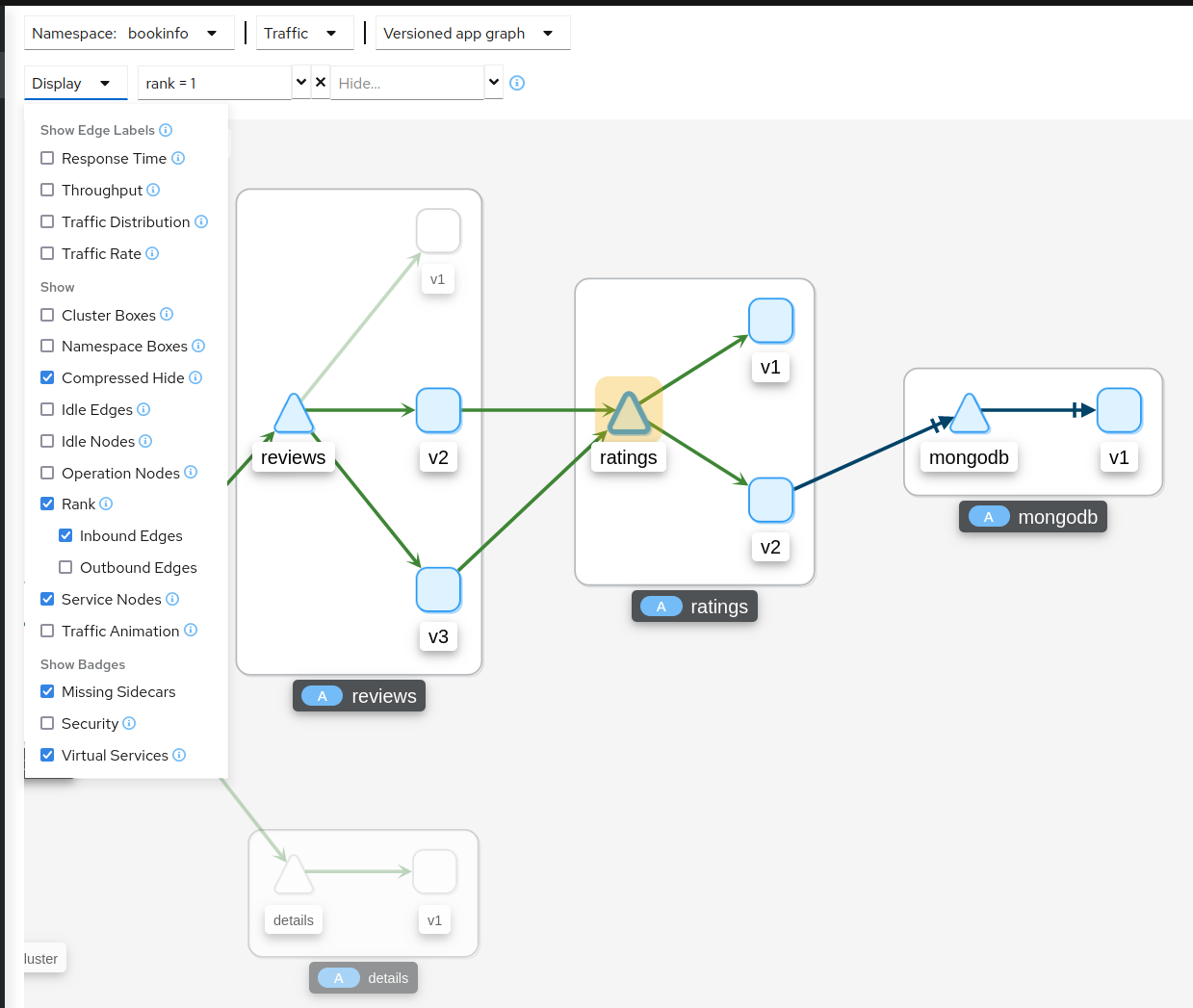
Ranking
Nodes can be ranked in the graph based on pre-defined criteria such as ‘number of inbound edges’. Combined with the find/hide feature, this allows you to quickly highlight or filter for important workloads, services, and applications.
Rankings are normalized to fit between 1..100 and nodes may tie with each other in rank. Ranking starts at 1 for the top ranked nodes so when ranking nodes based on ‘number of inbound edges’, the node(s) with the most inbound edges would have rank 1. Node(s) with the second most inbound edges would have rank 2. Each selected criteria contributes equally to a node’s ranking. Although 100 rankings are possible, only the required number of rankings are assigned, starting at 1.
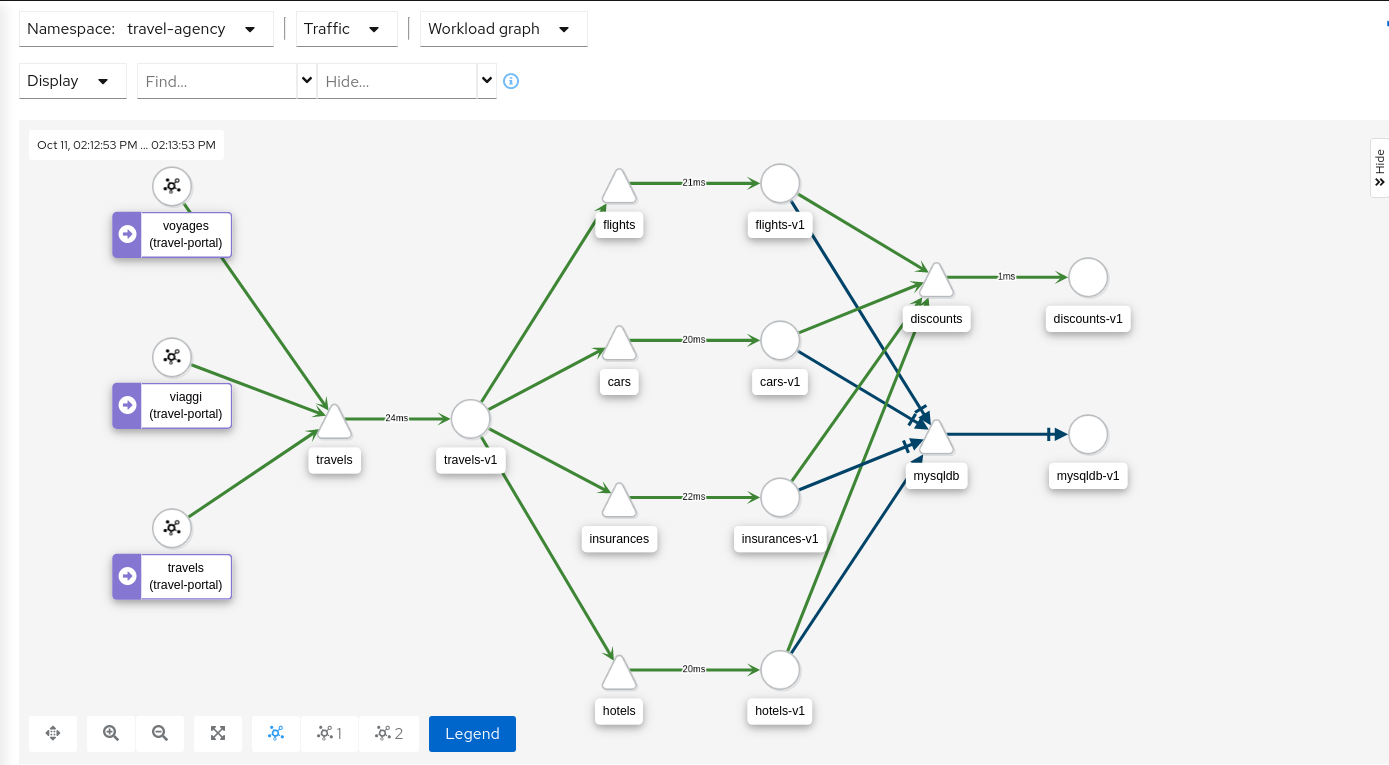
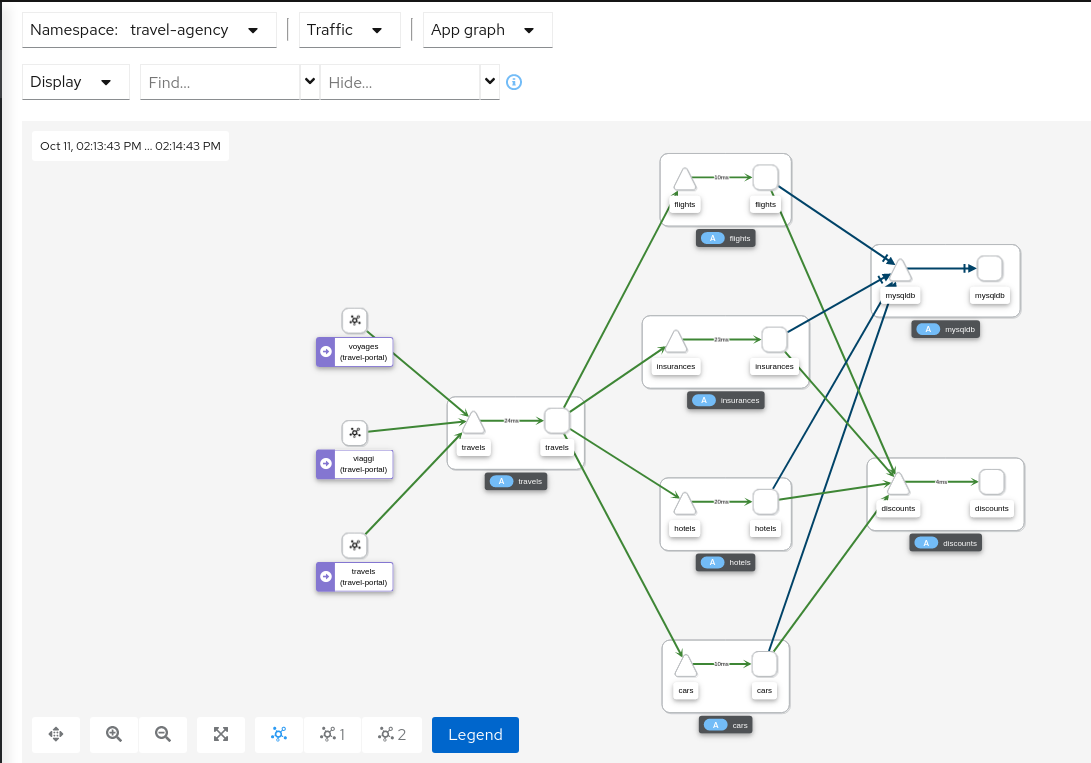
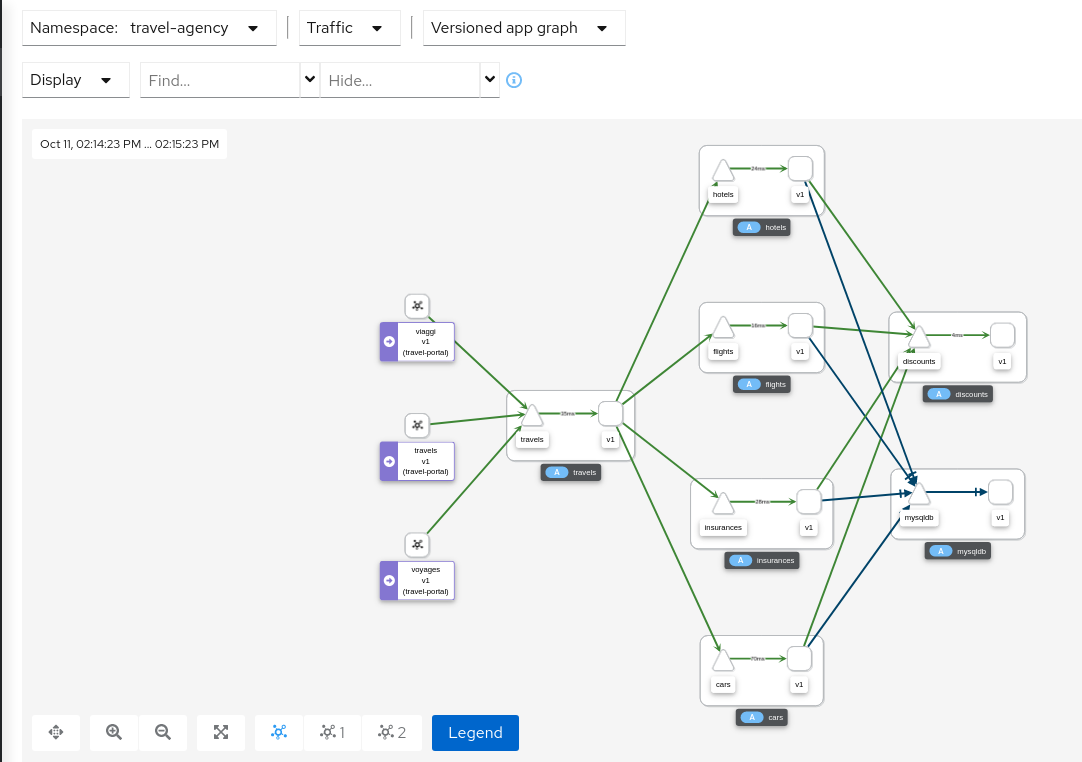
Graph Types
Kiali offers four different traffic-graph renderings:
-
The workload graph provides the a detailed view of communication between workloads.
-
The app graph aggregates the workloads with the same app labeling, which provides a more logical view.
-
The versioned app graph aggregates by app, but breaks out the different versions providing traffic breakdowns that are version-specific.
-
The service graph provides a high-level view, which aggregates all traffic for defined services.
Replay
Graph replay allows you to replay traffic from a selected past time-period. This gives you a chance to thoroughly examine a time period of interest, or share it with a co-worker. The graph is fully bookmarkable, including replay.
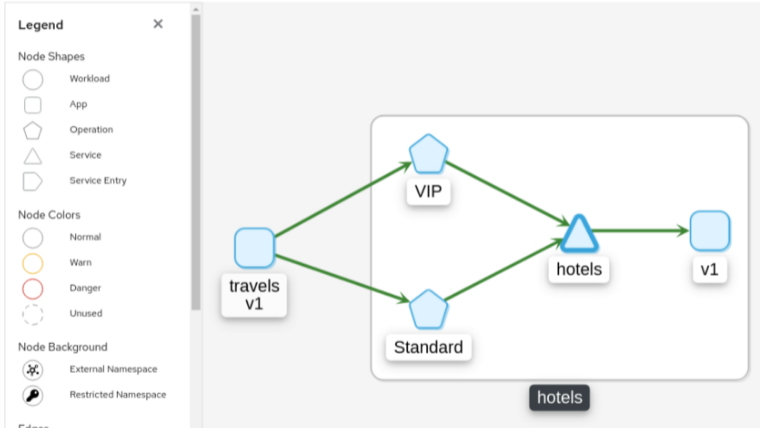
Operation Nodes
Istio v1.6 introduced Request Classification. This powerful feature allows users to classify requests into aggregates, called “Operations” by convention, to better understand how a service is being used. If configured in Istio the Kiali graph can show these as Operation nodes. The user needs only to enable the “Operation Nodes” display option. Operations can span services, for example, “VIP” may be configured for both CarRental and HotelRental services. To see total “VIP” traffic then display operation nodes without service nodes. To see “VIP” traffic specific to each service then also enable the “Service Nodes” display option.
When selected, an Operation node also provides a side-panel view. And when double-clicked a node detail graph is also provided.
Because operation nodes represent aggregate traffic they are not compatible with Service graphs, which themselves are already logical aggregates. For similar reasons response time information is not available on edges leading into or out of operation nodes. But by selecting the edge the response time information is available in the side panel (if configured).
Operation nodes are represented as pentagons in the Kiali graph: